- The mass on a particle is reduced using the time constant approach
- The decay constant is defined by the half-life
- Doses are computed from published conversion factors by radionuclide
- There are limitations to this simple approach:
- Decay does not start until the particle is emitted
- For continuous emissions, the emission rate must be decay corrected
- Concentration and deposition are decayed during the calculation
- Concentration and deposition are NOT decayed after file output
captex_control.txt | load control file |
captex_setup.txt | load setup file |
25 | run duration |
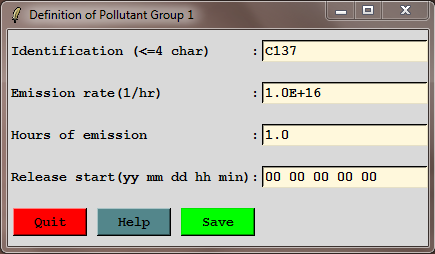
C137 | pollutant ID |
1.0E+16 | emission rate (Bq) |
1.0 | emission hours |
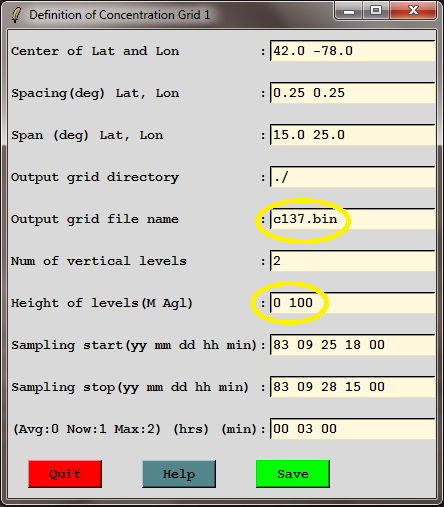
c137.bin | output grid name |
2 | number of levels |
0 100 | height of levels |
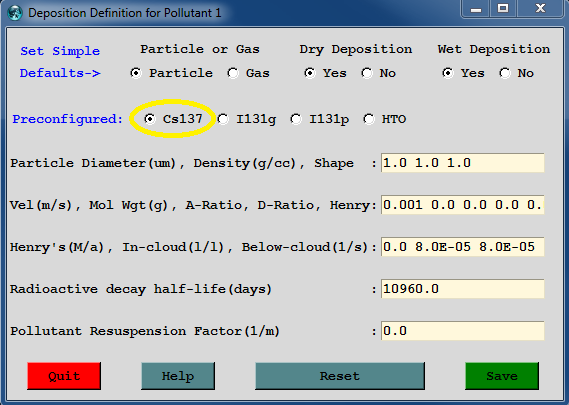
Select Cs-137
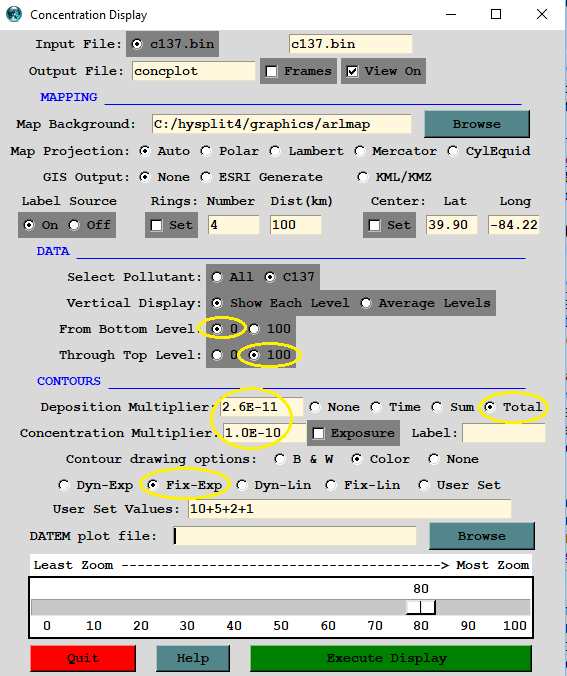
2.6E-11 | deposition multiplier (1.1E-12 rem/h x 24h) |
1.0E-10 | concentration multiplier 3.4E-11 rem/h x 3h) |
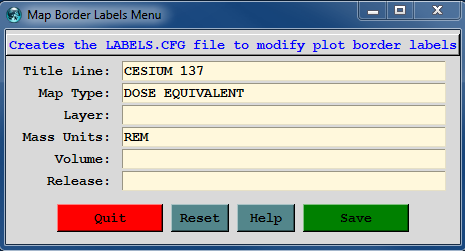
Dose Equivalent | border labels map type |
REM | border labels mass units |
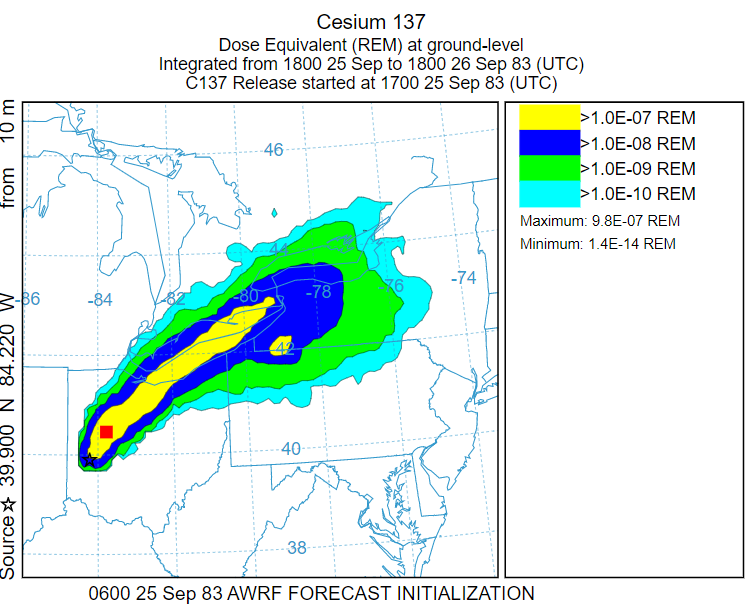
24-h dose
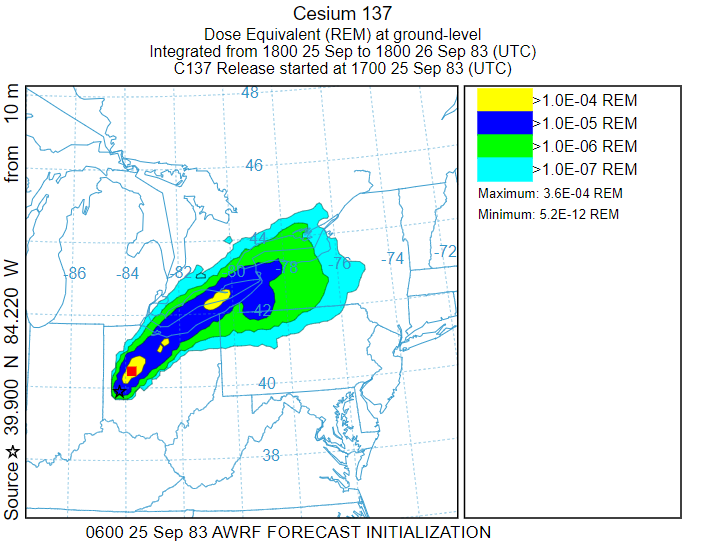
1-year dose
9.6E-09 | deposition multiplier (1.1E-12 rem/h x 8760h) |
|







